
Smart Factory – Smart Factory Glossary
The term Smart Factory refers to a "self-organizing production environment". So, the Smart Factory is the core piece of Industry 4.0. In a Smart Factory, machines, information technology, telecommunication, and sensors must be networked. Only if everything is networked, production systems can communicate with each other, exchange information on the manufacturing process and respond automatically to changes in production. In a nutshell, it can be said that "in a Smart Factory, not only the material but also the information must flow" (Kletti & Rieger, 2022, page 19). A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) like MPDV's HYDRA X that collects and processes data in real time is indispensable in the Smart Factory.
Thanks to the transparency provided by an MES, companies can respond to changes at an early stage and:
- avoid bottlenecks
- exploit resources effectively
- make faster decisions
All efforts are aimed at optimizing and automating the entire manufacturing process to achieve higher efficiency, quality, and flexibility. Different technologies must interact in order to collect, analyze, and use data in real time. Therefore, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, Big Data, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) are also of utmost importance in the Smart Factory.
Smart Factory and interoperability
Machines and systems must communicate properly with each other in order to ensure smooth operation of the Smart Factory. That is why, interoperability is a decisive factor in the Smart Factory. Interoperability ensures that different systems and applications can interact and share data to accomplish a common task. The Manufacturing Integration Platform (MIP) by MPDV exactly meets these requirements: It acts as a data hub for modern production IT and allows any combination of applications from different manufacturers. For this to work, all participants involved have the same understanding of data. This way all components can interact smoothly and help increase production efficiency.
Apart from smooth machine communication, it is also vital that data can be exchanged across various locations. A future-proof Manufacturing Execution System must therefore be able to reliably exchange production data with the MES of another site.

The role of humans in the Smart Factory
People still play a significant role in the Smart Factory even though they no longer intervene in the actual manufacturing process. For it is still the task of people to implement and operate new technologies. They also control workflows and optimize processes. People use KPIs to check if improvement measures take effect and intervene appropriately if deviations occur. This ensures a continuous improvement process (CIP). However, the field of activity of people working in production is changing as the mentioned tasks require to some extent new skills and qualifications.
Benefits of the Smart Factory
The benefits of the Smart Factory are diverse and support companies in staying competitive in times of changed conditions, such as disrupted supply chains, transportation problems or increasing energy prices. In the end, the Smart Factory is a major step towards a future-proof and sustainable production. Companies investing in this technology can expand their competitive edge and prepare for future challenges:
- Increase productivity and efficiency
- Reduce production costs
- Improve quality and flexibility
The MPDV Group helps you succeed in the Smart Factory
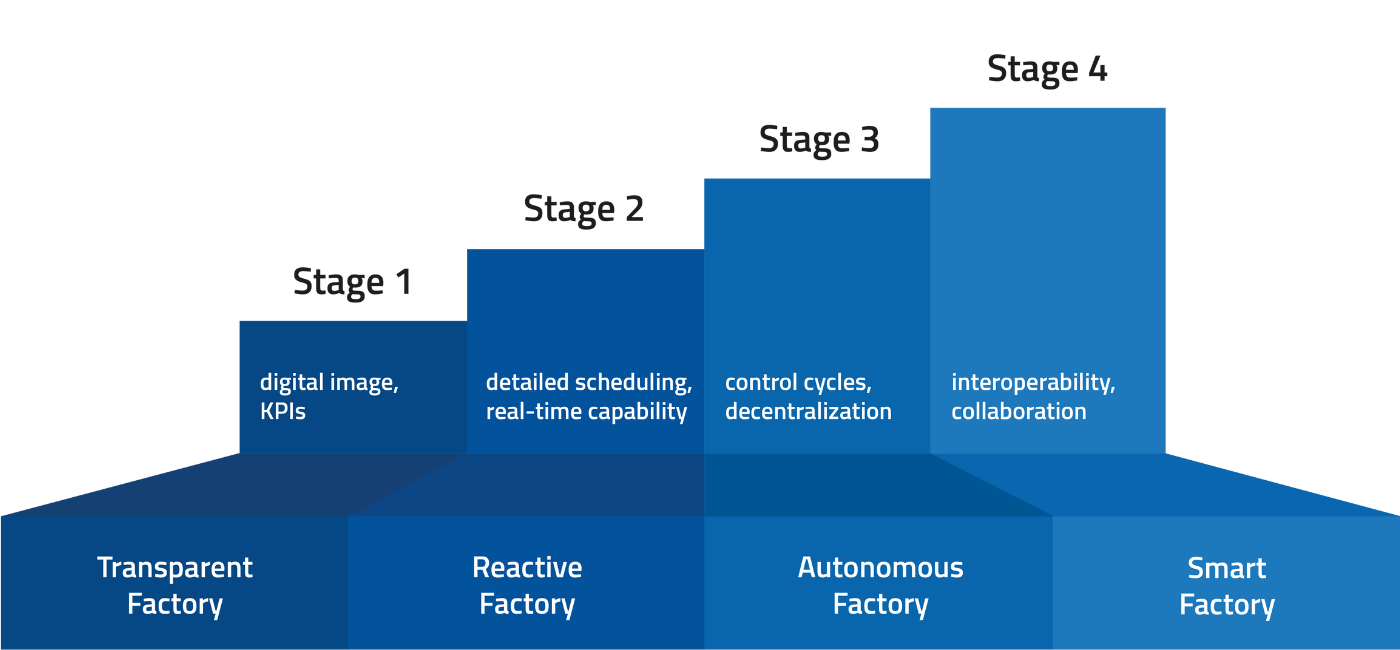
MPDV's four-stage model describes how companies can turn their factory into a Smart Factory. According to the model, transparency in production is key so every employee knows what is currently happening. All other steps are based on this principle. The second stage aims at creating a reactive factory: data is aggregated, analyzed, and visualized to be able to respond quickly and appropriately to malfunctions. The third stage converts production into a self-regulating factory where production processes are controlled automatically. The Smart Factory is complete once the factory is functionally networked, i.e. the network also integrates adjacent processes and systems. The white papers on this subject provide detailed information on the single stages.
The four building blocks of perfect production provide further guidance on the way to the Smart Factory:
- Building block 1: value stream management 4.0
- Building block 2: lean value streams
- Building block 3: lean support features
- Building block 4: sustainable process improvement
Even though a Manufacturing Execution System is considered the basis for the Smart Factory, it is by far not enough to just implement the system in the production company. First of all, the company must create the organizational framework conditions so that MES software such as HYDRA X can be used effectively and sustainably. To do so, existing processes and value streams must first be scrutinized and streamlined before digitalization of processes can be started. For only a good analog process can become a good digital process. The management consultancy, Perfect Production GmbH, supports companies in digitalizing their production and is a reliable partner for value stream management 4.0 and lean methods.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Smart Factory
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in the Smart Factory: it can help companies to significantly improve the efficiency and flexibility of their production processes. For this purpose, AI systems analyze big data to identify patterns and make predictions. AI technology enables predictive maintenance, for example, which reduces downtime. AI also supports the automation of complex tasks, improves quality assurance by precisely identifying defects, and enables adaptive production planning.
MPDV has combined numerous standard AI applications in the AI Suite. Interaction with the Manufacturing Execution System HYDRA X or the Advanced Planning and Scheduling System FEDRA enables rapid optimization. Of particular significance is the AI-supported planning, which has been shown to increase adherence to delivery dates. Other applications promise to predict product quality, identify, and understand correlations that lead to scrap, or determine realistic default values to improve planning results.
Would you like more information? We are happy to help.
Send us an e-mail. We will take care of your inquiry promptly.