Total Productive Maintenance / TPM – Smart Factory Glossary
Total Productive Maintenance, TPM for short, is a method of performing preventive maintenance and repairs on machines. Preventive maintenance strategies are designed to minimize unplanned downtime. The primary objective is to increase the availability of production equipment (see Overall Equipment Effectiveness / OEE).
Total Productive Maintenance is a lean management approach based on a comprehensive strategy. In addition to preventive maintenance, the TPM method relies on close cooperation between different departments. All employees are actively involved in the maintenance process.
Objective Total Productive Maintenance
Total Productive Maintenance pursues key objectives that contribute to significantly increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing processes. Ultimately, TPM aims to create a zero-defect, zero-failure, and zero-accident environment.
- Increasing machine availability: Through systematic maintenance and preventive maintenance strategies, TPM aims to maximize machine uptime and minimize unplanned downtime and thereby increasing productivity and reliability in production.
- Improving equipment efficiency: TPM aims to make optimal use of all resources and technical equipment. By continuously monitoring equipment and implementing targeted improvement measures, overall equipment effectiveness is increased.
- Reducing manufacturing defects: By integrating Total Productive Maintenance practices from quality management, you can ensure that your machines produce high-quality products without defects and at the same time reduce rework and scrap. These measures reduces rework and scrap and improves customer satisfaction.
- Ensuring occupational safety: The safety of machines and equipment is regularly checked, and potential hazards are identified and eliminated. This helps keep the workplace safe and minimizes accidents and health risks.
- Promote employee participation: All employees take on an active part in the maintenance process. Ongoing training develops their skills so that everyone involved can play an active role in machine maintenance. This gives people a stronger sense of responsibility and helps keep production processes running smoothly.
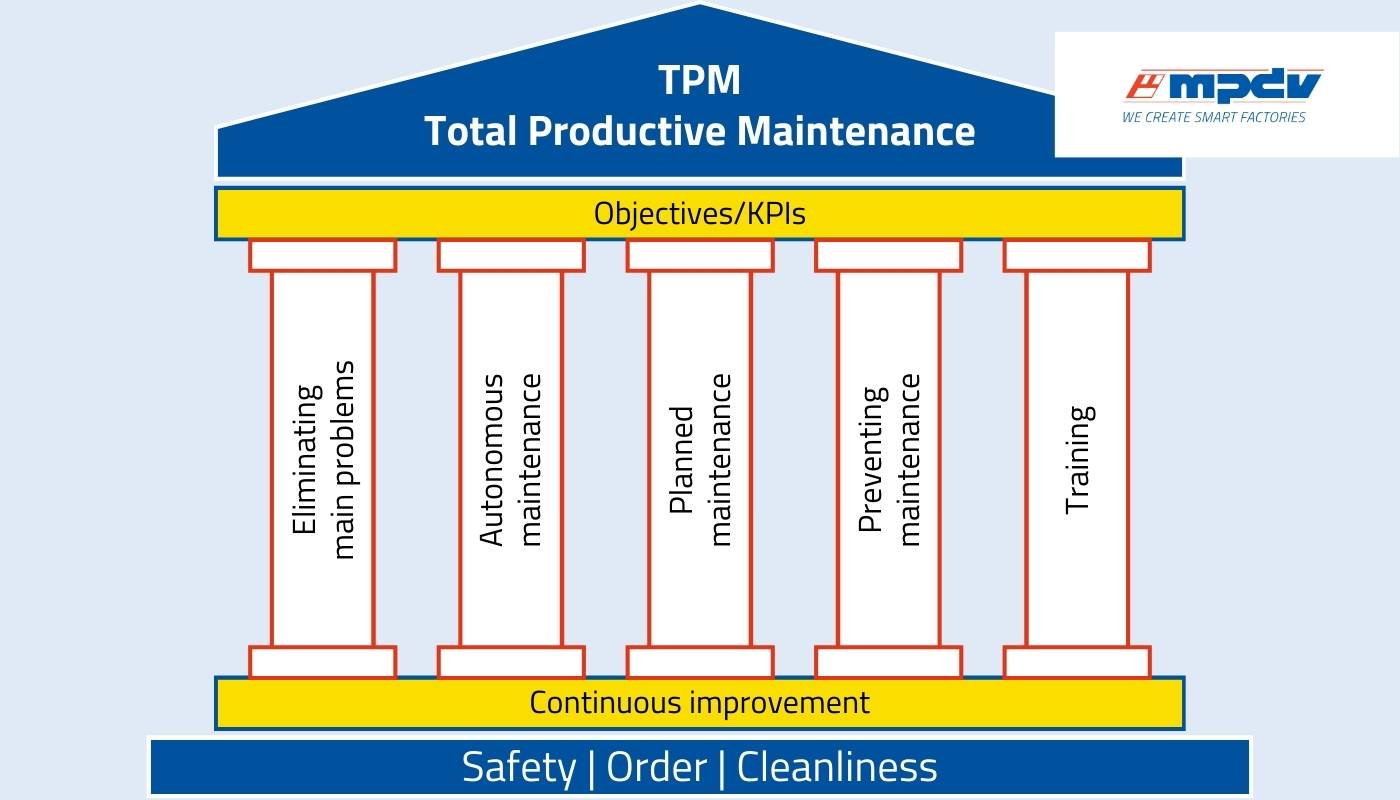
Five pillars of Total Productive Maintenance
The traditional TPM model is based on the 5S principles, which stand for organization, cleanliness, development, maintenance, and discipline in the workplace – achieved with an upstream 5S project. To get the best results, continuous improvement is key.
- Elimination of key problems: This pillar focuses on identifying and solving fundamental problems that impair the efficiency and performance of machines. These are often recurring problems or weak points in production. Focus is on availability, performance, and quality losses. You can quantify losses using Machine Data Collection in a Manufacturing Execution System.
Autonomous maintenance: Machine operators perform basic maintenance tasks such as cleaning and inspection to detect signs of wear or potential failures at an early stage. This approach not only promotes a better understanding of your own machines, but also reduces dependence on specialized maintenance teams for everyday checks. Digital checklists are a useful tool for taking all critical points into account and documenting the results.
- Planned maintenance: This pillar addresses the issue of reducing unplanned machine downtime. For this purpose, regular maintenance work is carefully planned and conducted. By implementing a systematic maintenance plan, the service life of machines is extended and unplanned downtime minimized.
- Preventive maintenance: This strategy aims to take future maintenance into account when machines are purchased and installed. For example: All maintenance points can be easily accessed.
- Training: Preventive maintenance depends entirely on the skills of the employees. Continuous development by means of targeted training and education programs therefore contributes significantly to the successful implementation of the TPM concept. A basic understanding of the OEE index is established so that employees can contribute to the best of their ability. On top of that, employees pick up skills in machine operation, maintenance, and problem solving, and can conduct maintenance work more effectively.
In fact, eight basic principles are often cited as the foundation of the TPM method: autonomous maintenance, continuous improvement, planned maintenance, quality management, equipment management, training and further education, occupational health and safety, and TPM in administrative processes.
TPM and MES
A Manufacturing Execution System such as MES HYDRA X from MPDV is ideal for providing digital support for the TPM method. By analyzing downtime and failures, the availability and performance of machines can be continuously improved. For companies looking to explore lean management and manufacturing excellence, the Executive Manufacturing Center (EMC) is the place to go. MPDV's consulting division provides tailored information on the positive effects on production and develops a corresponding roadmap.
Source
- Total Productive Maintenance: Wikipedia, 09.02.2025 [online] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Total_productive_maintenance (accessed on 03.13.2025).
Would you like more information? We are happy to help.
Send us an e-mail. We will take care of your inquiry promptly.